Types of Breast Cancer
Types of Breast Cancer
There are several different types of breast cancer. In this section, we will discuss some types of breast cancer and describe their main characteristics.
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS)
- Also known as intraductal carcinoma
- Non-invasive breast cancer
- Abnormal cells have not spread through the ducts into surrounding breast tissue
- Has not yet spread outside of breast
- May become invasive breast cancer
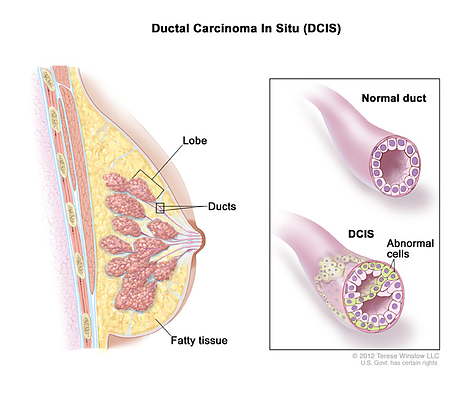
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), solid type. The cells are larger than in LCIS and are filling the ductal rather than the lobular spaces. However, the cells are contained within the basement membrane of the duct and do not invade the breast stroma.
DCIS is more morphologically heterogeneous than LCIS, and pathologists recognize four broad types of DCIS: papillary, cribriform, solid, and comedo. For more detailed coverage of DCIS you may want to read:Boyages, J. (2014). DCIS of the Breast: Taking Control. Beecroft, NSW: BC Publishing.
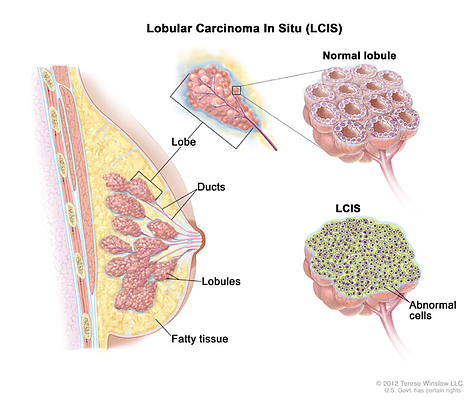
Lobular Carcinoma in Situ (LCIS)
- Also called lobular neoplasia
- Abnormal cell growth starts in the lobules of the breast
- LCIS is regarded as a risk factor for the development of breast cancer. LCIS is recognized by its conformity to the outline of the normal lobule, with expanded and filled acini
- Not considered a true cancer because it is not likely to spread to surrounding tissues
- LCIS is an indicator that a woman may be more likely to develop invasive cancer in either breast
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC)
- Also known as infiltrating ductal carcinoma
- Most common type of breast cancer
- Starts in the ducts of the breast, then grows into fatty breast tissue
- May also spread to other parts of the body through the lymph system and bloodstream
- Approximately 8 out of 10 invasive breast cancers are invasive ductal carcinomas
- Invasive ductal cancer, also known as infiltrating ductal carcinoma, is the most common form of breast cancer; it accounts for 50% to 70% of invasive breast cancers.
- When invasive ductal carcinomas take on differentiated features, they are named according to the features that they display. If the infiltrating cells form small glands lined by a single row of bland epithelium, they are called infiltrating tubular carcinoma. The infiltrating cells may secrete copious amounts of mucin and appear to float in this material. These lesions are called mucinous or colloid tumors. Tubular and mucinous tumors are usually low-grade (grade I) lesions; these tumors each account for approximately 2% to 3% of invasive breast carcinomas.
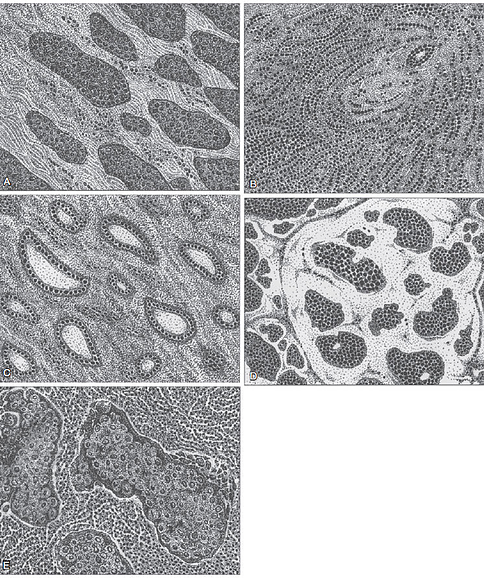
Invasive breast cancer. A, Invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified. The malignant cells invade in haphazard groups and singly into the stroma. B,Invasive lobular carcinoma. The malignant cells invade the stroma in a characteristic single-file pattern and may form concentric circles of single-file cells around normal ducts (targetoid pattern). C, Invasive tubular carcinoma. The cancer invades as small tubules, lined by a single layer of well-differentiated cells. D, Mucinous or colloid carcinoma. The bland tumor cells float like islands in lakes of mucin. E, Medullary carcinoma. The tumor cells are large and very undifferentiated, with pleomorphic nuclei. The distinctive features of this tumor are the infiltrate of lymphocytes and the syncytium-appearing sheets of tumor cells.dd your own text and edit me. It’s easy.
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC)
- Also known as infiltrating ductal carcinoma
- Most common type of breast cancer
- Starts in the ducts of the breast, then grows into fatty breast tissue
- May also spread to other parts of the body through the lymph system and bloodstream
- Approximately 8 out of 10 invasive breast cancers are invasive ductal carcinomas
- Invasive ductal cancer, also known as infiltrating ductal carcinoma, is the most common form of breast cancer; it accounts for 50% to 70% of invasive breast cancers.
- When invasive ductal carcinomas take on differentiated features, they are named according to the features that they display. If the infiltrating cells form small glands lined by a single row of bland epithelium, they are called infiltrating tubular carcinoma. The infiltrating cells may secrete copious amounts of mucin and appear to float in this material. These lesions are called mucinous or colloid tumors. Tubular and mucinous tumors are usually low-grade (grade I) lesions; these tumors each account for approximately 2% to 3% of invasive breast carcinomas.

Invasive breast cancer. A, Invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified. The malignant cells invade in haphazard groups and singly into the stroma. B,Invasive lobular carcinoma. The malignant cells invade the stroma in a characteristic single-file pattern and may form concentric circles of single-file cells around normal ducts (targetoid pattern). C, Invasive tubular carcinoma. The cancer invades as small tubules, lined by a single layer of well-differentiated cells. D, Mucinous or colloid carcinoma. The bland tumor cells float like islands in lakes of mucin. E, Medullary carcinoma. The tumor cells are large and very undifferentiated, with pleomorphic nuclei. The distinctive features of this tumor are the infiltrate of lymphocytes and the syncytium-appearing sheets of tumor cells.dd your own text and edit me. It’s easy.
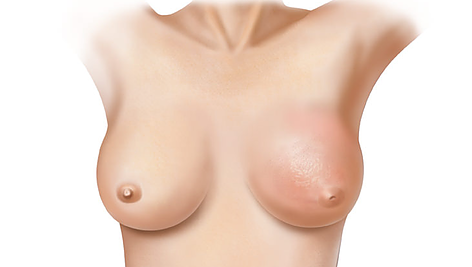
Inflammatory Breast Cancer
- Uncommon type of invasive breast cancer
- Approximately accounts for 1% to 3% of all breast cancers
- A lump or tumor is not always detected
- Cancer cells block lymph vessels in the skin and cause skin irritation
- Symptoms may consist of:
- Inflammation
- Redness
- Pitted appearance
- Itchiness
- Tenderness
Paget Disease
- Rare type of breast cancer
- Approximately accounts for 1% of all breast cancers
- Cancer starts in the breast ducts, then spreads to the skin of the nipple, and areola
- Usually associated with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC)
- Symptoms may consist of the nipple and areola being:
- Crusted
- Scaly
- Red
- Bleeding or oozing
- Burning
- Itching
Types of Breast Cancer
References
